Lateral Femoral Condyle Friction Syndrome
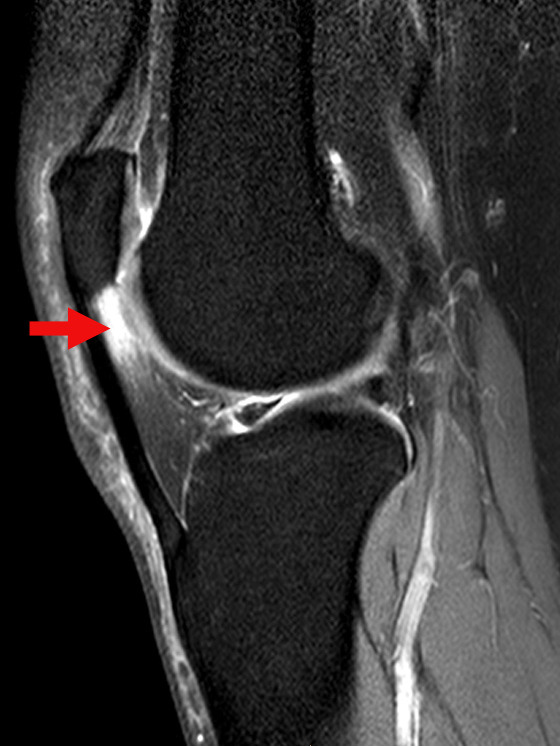
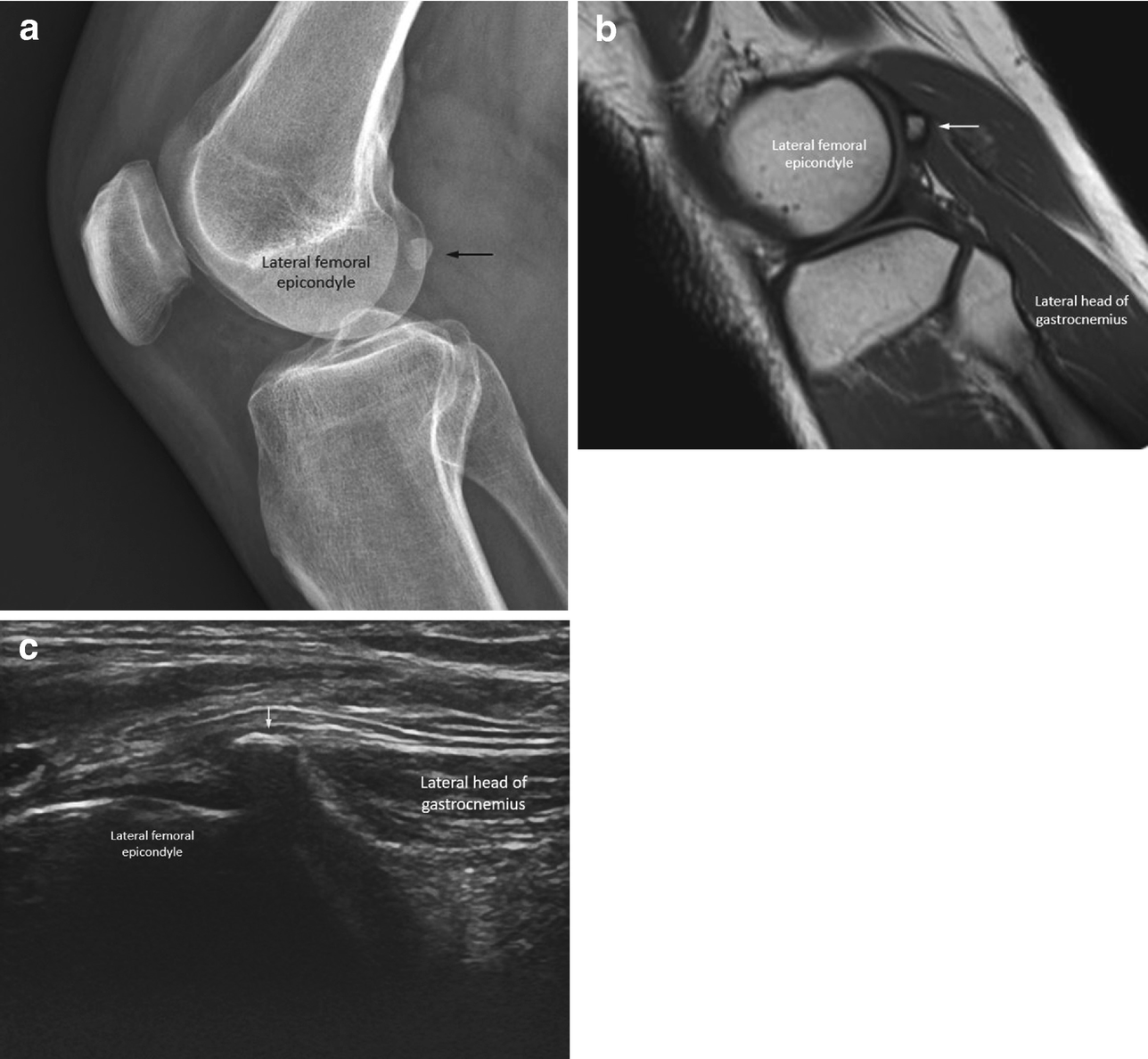
Lateral femoral condyle friction syndrome. It is thought to be due to patella maltracking or imbalance of the forces between medial and lateral vastus muscles causing impingement of the superolateral aspect of Hoffa fat pad between the inferior patella and the lateral femoral condyle. A condition characterized by excessive friction between the iliotibial band and the lateral femoral condyle. There was evidence of a high-riding patella patellar malalignment and patellar tendon-lateral femoral condyle friction syndrome with significantly close contact between the patellar tendon and the lateral facet of the femoral trochlea.
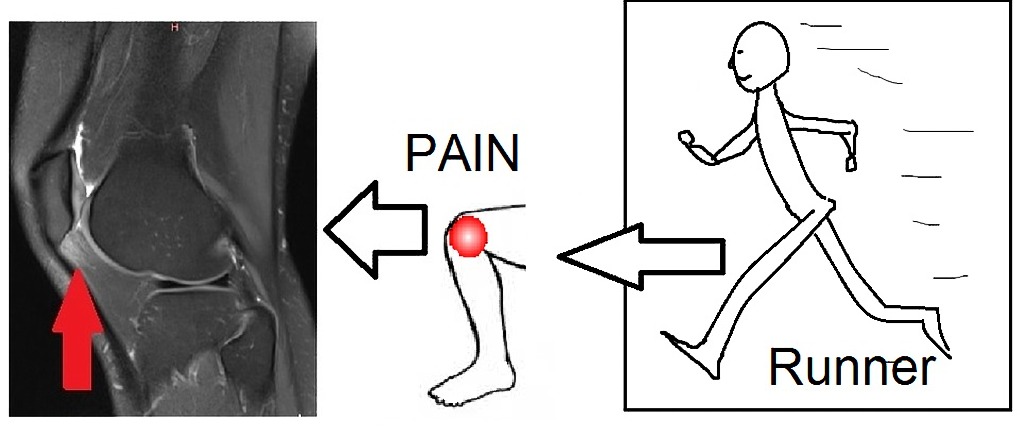
Patellar tendon-lateral femoral condyle friction syndrome also known as Hoffa fat pad impingement syndrome is a common cause of anterior knee pain in active individuals. 35 Several causes have been suggested and the friction theory of repetitive ITB motion against the lateral femoral epicondyle during knee flexion and extension is most widely accepted. Comprises 2-15 of all overuse injuries of the knee.
To demonstrate the MR imaging findings that occur between the posterior inferolateral patellar tendon and the lateral femoral condyle in patients with chronic anterior and or lateral knee pain. Due to trauma or altered biomechanics or wear and tear inflammation the anterior fat pad of your knee gets pinched between the femoral condyle and th. MRI findings of a patellar tendon-lateral femoral condyle friction syndrome also known as Hoffas fat pad impingement syndrome with associated patella Alta and bucket handle lateral meniscal tear.
Keegan Duchicela answered 14 years experience Family Medicine Hoffas syndrome. Sharp margin of antero-inferior lateral femoral condyle as a risk factor for patellar tendon-lateral femoral condyle friction syndrome. 1 public playlist include this case.
Keegan Duchicela answered 14 years experience Family Medicine Hoffas syndrome. ITB syndrome is an overuse syndrome and the most common etiology of lateral knee pain in runners. Due to trauma or altered biomechanics or wear and tear inflammation the anterior fat pad of your knee gets pinched between the femoral condyle and th.
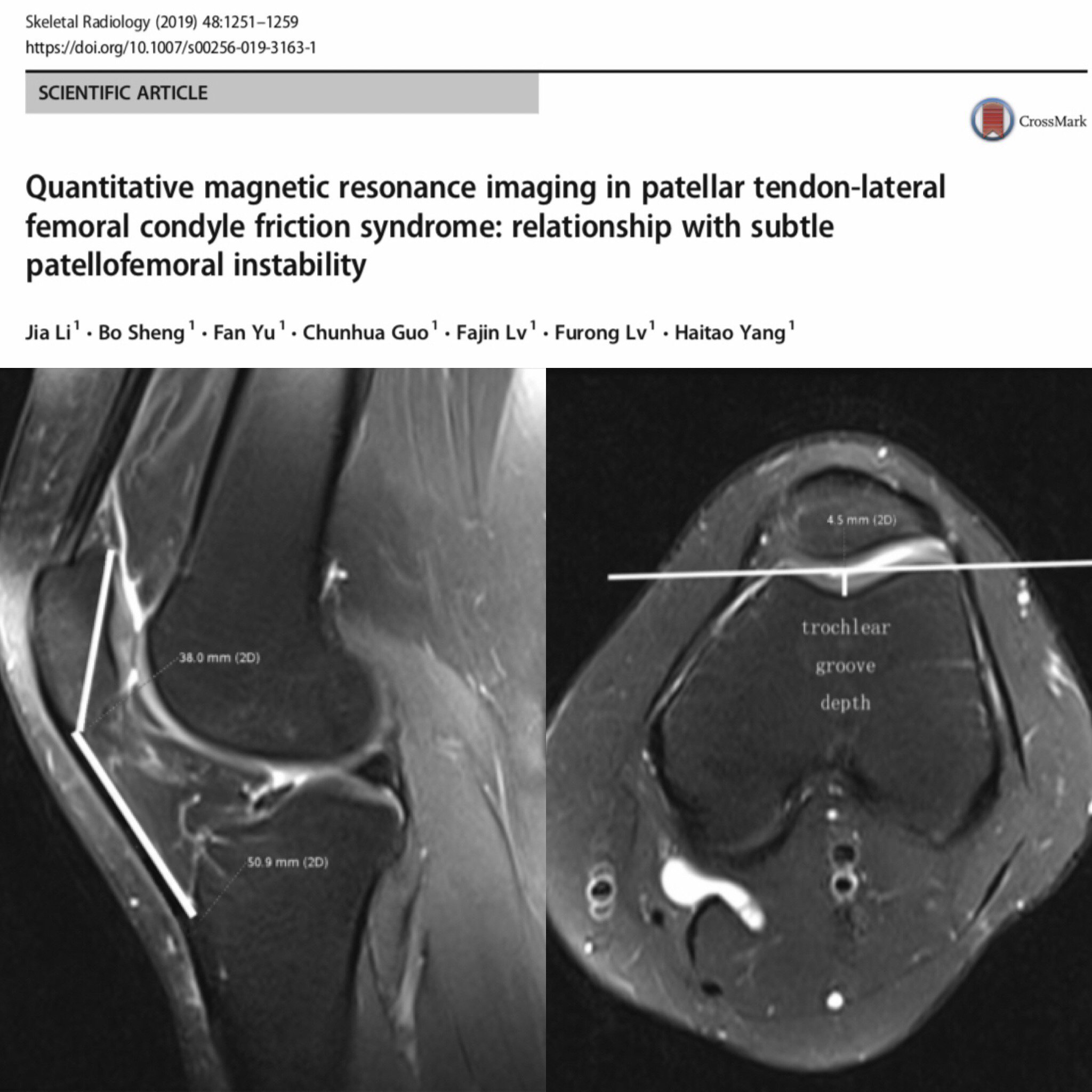
Li J 1 Sheng B 1 Liu X 1 Yu F 1 Lv F 1 Lv F 1 Yang H 2. What is petellar tendon lateral femoral condyle friction syndrome and how is it treated. Patellar tendon-lateral femoral condyle friction syndrome Hoffa fat pad impingement is thought to be an overuse injury characterized by direct contact of the patellar tendon against the lateral femoral condyle causing compression of the superolateral aspect of the infrapatellar fat pad.
36 Anatomic factors that biomechanically predispose patients to this condition include excessive genu varum. Patellar tendon-lateral femoral condyle friction syndrome also known as Hoffa fat pad impingement syndrome is a common cause of anterior knee pain in active individuals.
Keegan Duchicela answered 14 years experience Family Medicine Hoffas syndrome.
MRI findings of a patellar tendon-lateral femoral condyle friction syndrome also known as Hoffas fat pad impingement syndrome with associated patella Alta and bucket handle lateral meniscal tear. There was evidence of a high-riding patella patellar malalignment and patellar tendon-lateral femoral condyle friction syndrome with significantly close contact between the patellar tendon and the lateral facet of the femoral trochlea. A condition characterized by excessive friction between the iliotibial band and the lateral femoral condyle. 12 The etiology of this syndrome is likely due to altered biomechanics and may be associated with patellar maltracking and a. What is petellar tendon lateral femoral condyle friction syndrome and how is it treated. 35 Several causes have been suggested and the friction theory of repetitive ITB motion against the lateral femoral epicondyle during knee flexion and extension is most widely accepted. 36 Anatomic factors that biomechanically predispose patients to this condition include excessive genu varum. A retrospective review of the MR images in 42 patients who presented with chronic anterior or lateral knee pain was performed by two musculoskeletal radiologists. 17 Some authors described similar MRI features and gave the name of patellar tendon-lateral femoral condyle friction syndrome which is also related to the clinical entity of fat pad.
What is petellar tendon lateral femoral condyle friction syndrome and how is it treated. A condition characterized by excessive friction between the iliotibial band and the lateral femoral condyle. 12 The etiology of this syndrome is likely due to altered biomechanics and may be associated with patellar maltracking and a. ITB syndrome is an overuse syndrome and the most common etiology of lateral knee pain in runners. Li J 1 Sheng B 1 Liu X 1 Yu F 1 Lv F 1 Lv F 1 Yang H 2. Patellar tendon-lateral femoral condyle friction syndrome also known as Hoffa fat pad impingement syndrome is a common cause of anterior knee pain in active individuals. Patellar tendon-lateral femoral condyle friction syndrome also known as Hoffa fat pad impingement syndrome is a common cause of anterior knee pain in active individuals.



























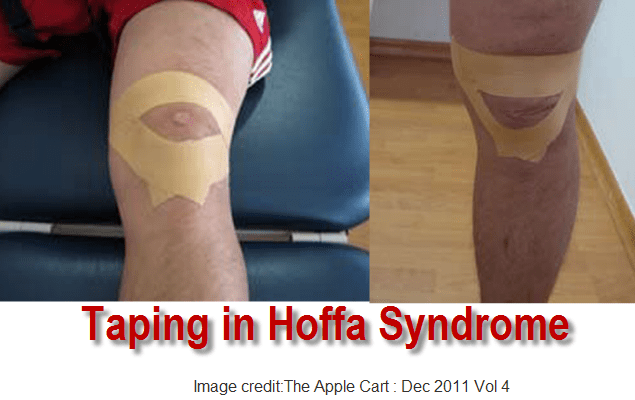

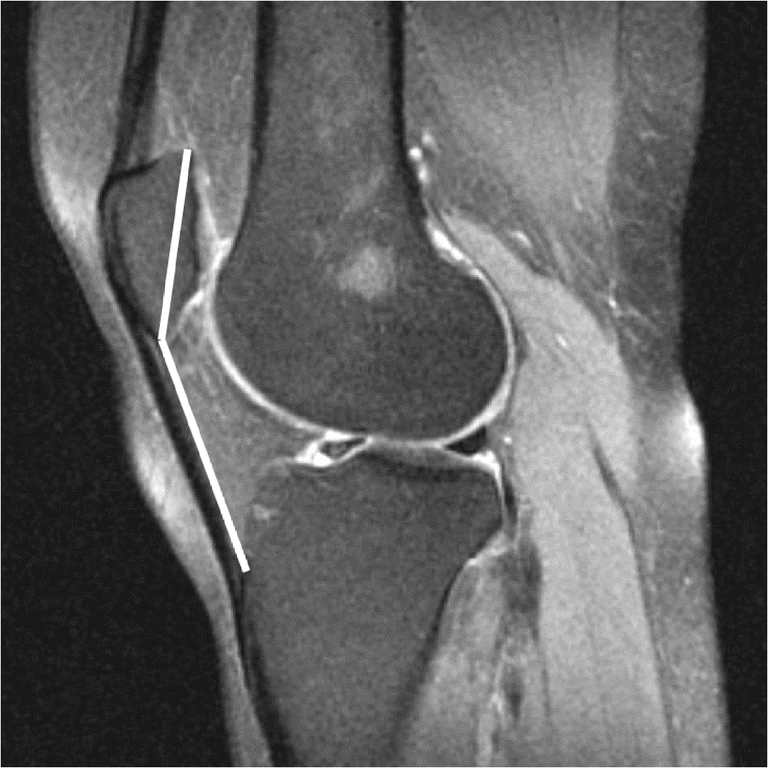




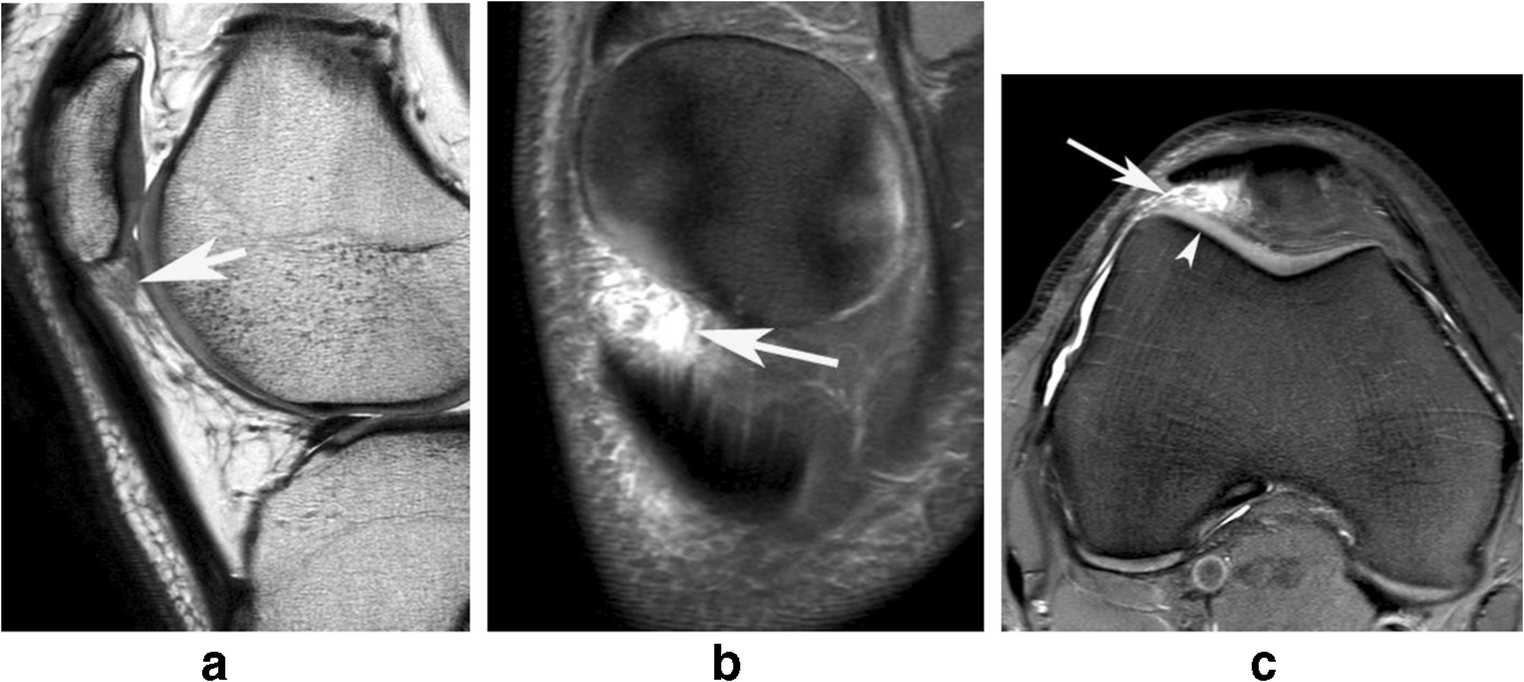

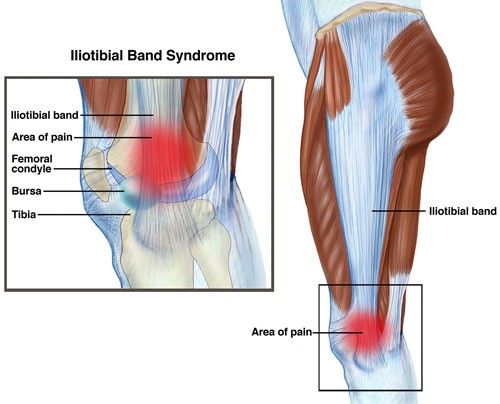


Post a Comment for "Lateral Femoral Condyle Friction Syndrome"