Charcot Marie Tooth Disease Radiology
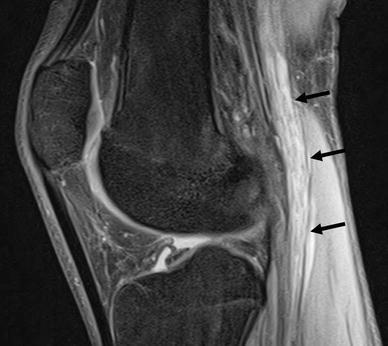
Charcot marie tooth disease radiology. X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease CMT1X is the second most common form of inherited neuropathy. Gallardo E Garcia A Combarros O Berciano J. MRI is an ideal method for identifying areas of muscle atrophy and fatty infiltration.
The peripheral nerves are found outside the main central nervous system brain and spinal cord. Patients develop a progressive distal weakness and atrophy that results from length-dependent axonal loss. Charcot-Marie-Tooth CMT disease is one of the.
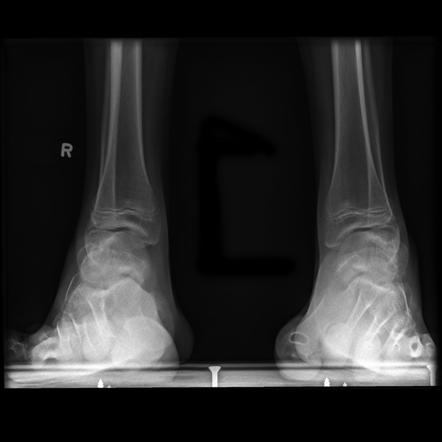
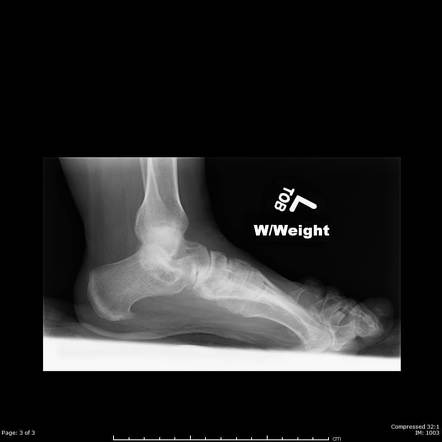
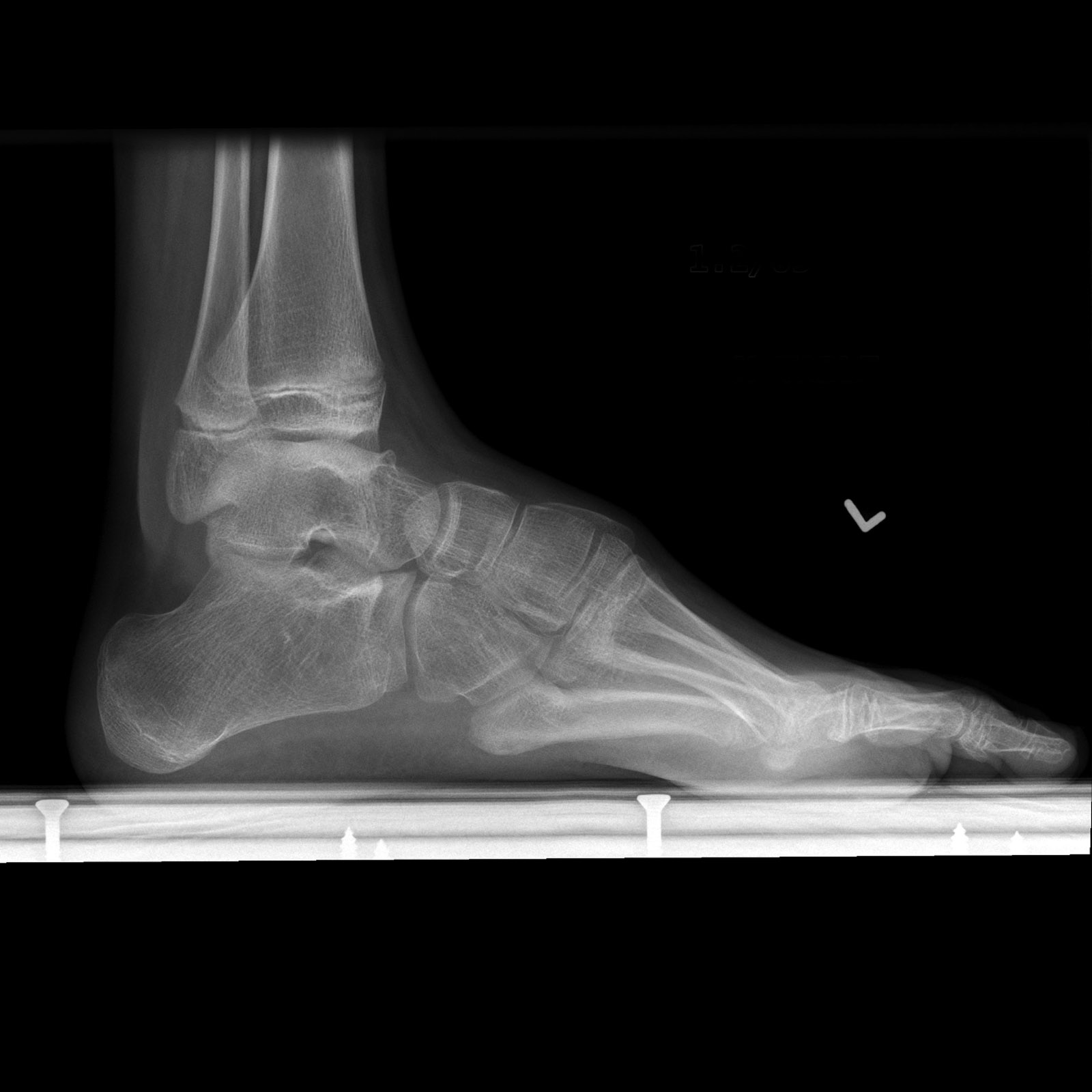
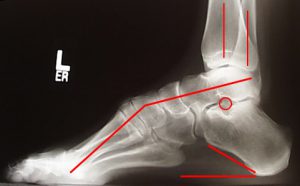
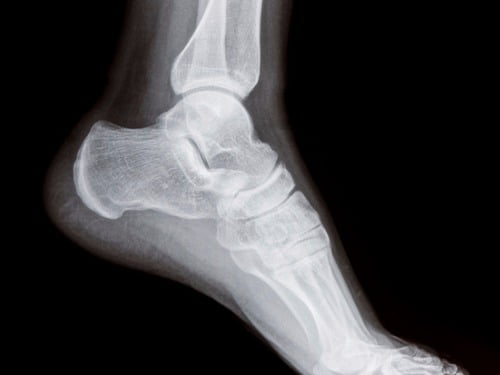
Atrophy associated with mild-to-moderate sensory loss. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease CMT is one of a group of disorders that cause damage to the peripheral nervesthe nerves that transmit information and signals from the brain and spinal cord to and from the rest of the body as well as sensory information such as touch back to the spinal cord and brain. Pes cavus and hammer toe deformities with twisting of the ankle.
Clinical manifestations include 123. Its also known as hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy HMSN or peroneal muscular atrophy PMA. Charcot-Marie-Tooth CMT disease is a group of hereditary sensory and motor neuropathies resulting from demyelination axonal dysfunction or both 123.
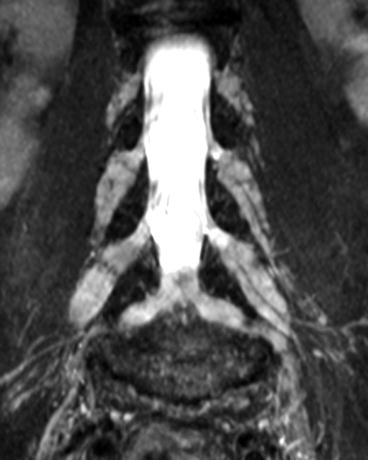
Charcot-Marie-Tooth CMT disease is one of the hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy HMSN disorders a group of genetically based disorders characterized by progressive motor weakness decreased nerve conduction velocities and nerve root enlargement 1. The finding of massive enlargement of the spinal nerve roots is demonstrated on a computed tomographic scan in. An epidemiological genetic study of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease in Western Japan.
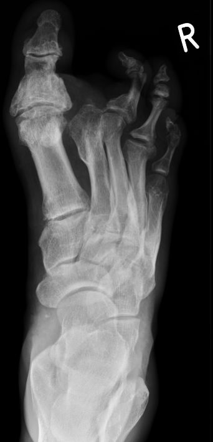
Severe atrophy of all intrinsic short foot muscles which have been replaced by fat tissue. Taken together results from these articles support the concept that genetic causes of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease serve as a living microarray system to identify molecules necessary for normal peripheral nervous system function. There is linear thickening of several cauda equina equina extending from the leve.
Spectrum of clinical and magnetic resonance imaging features in. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A duplication.
Charcot-Marie-Tooth CMT disease is the most common inherited neuromuscular disorder.
Gallardo E Garcia A Combarros O Berciano J. Severe atrophy of all intrinsic short foot muscles which have been replaced by fat tissue. CharcotMarieTooth disease CMTD also known as hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy HMSN is the most frequent form of inherited polyneuropathy with a prevalence ratio of 17-40 cases per 100 000 inhabitants. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease is a hereditary hypertrophic neuropathy. Pes cavus and hammer toe deformities with twisting of the ankle. MR and CT imaging has become more common in the evaluation of CMT to identify areas of disease involvement. What is Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Its also known as hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy HMSN or peroneal muscular atrophy PMA. Distal muscle weakness.
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A duplication. It is characterized by inherited neuropathies without known metabolic derangements. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease is a hereditary hypertrophic neuropathy. CMTD is caused by different gene mutations that produce modified proteins that affect peripheral axon or myelin. An epidemiological genetic study of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease in Western Japan. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease CMT is a group of inherited conditions that damage the peripheral nerves. Taken together results from these articles support the concept that genetic causes of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease serve as a living microarray system to identify molecules necessary for normal peripheral nervous system function.



























Post a Comment for "Charcot Marie Tooth Disease Radiology"