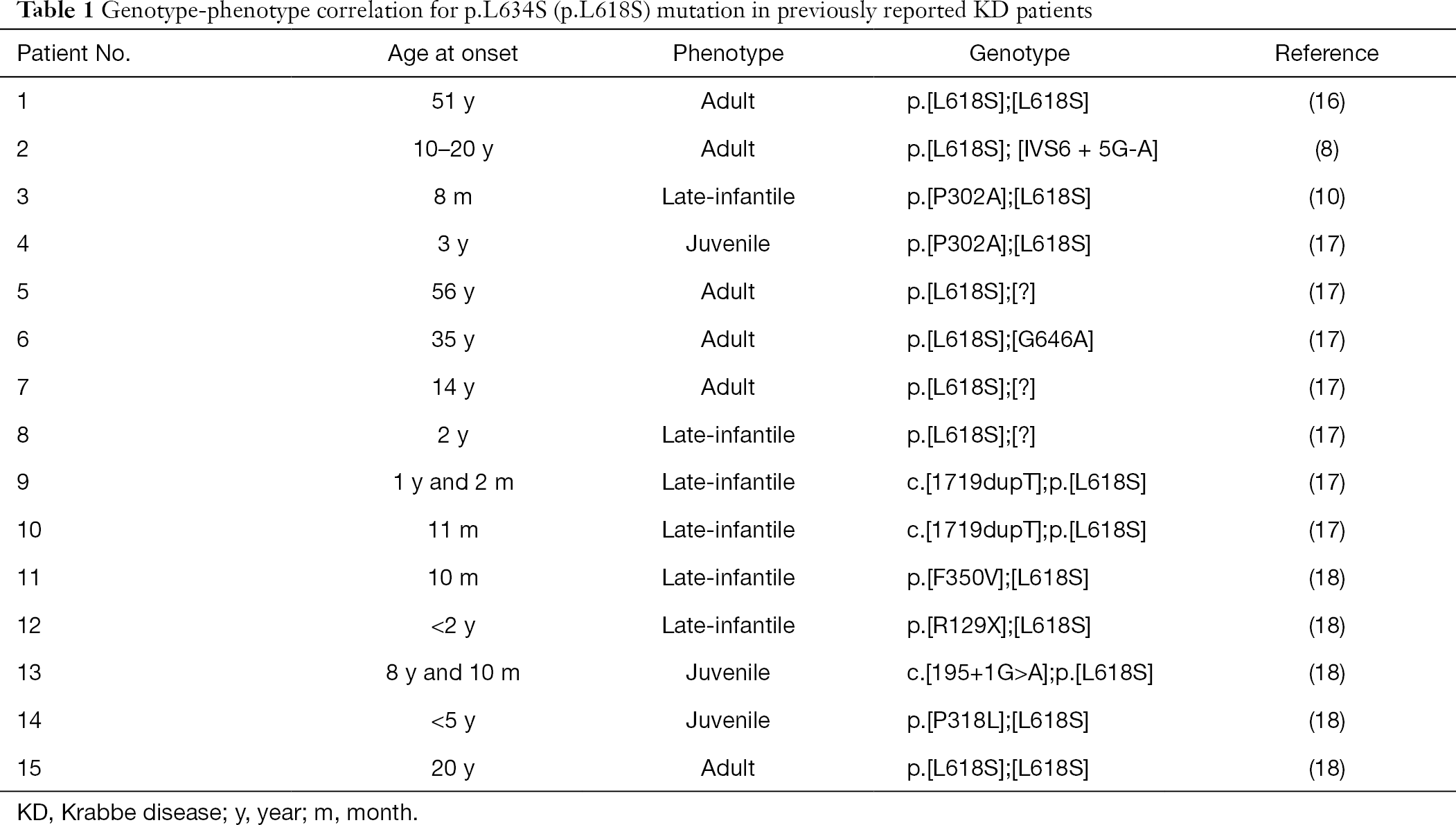
Krabbe Disease In Adults
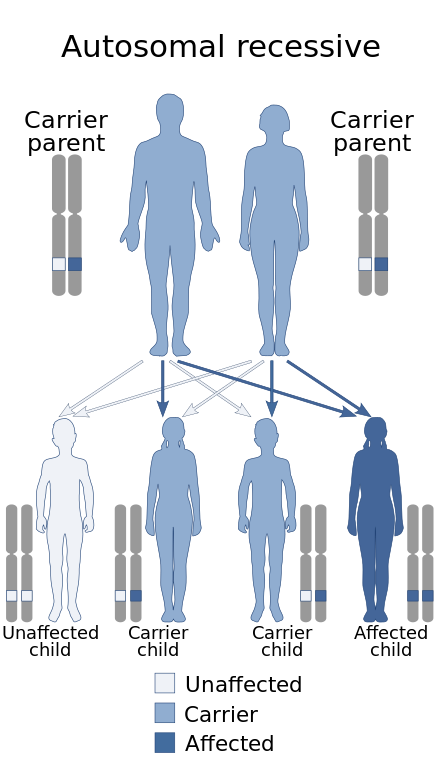
Krabbe disease in adults. Krabbe disease is an autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disease caused by deficiency of the β-galactocerebrosidase enzyme which leads to oligodendrocyte apoptosis and gliosis. Patients diagnosed after the age of 16 years were included in this study. Other signs of the disease include peripheral neuropathy dysarthria cerebellar ataxia pes cavus deep sensory signs tongue atrophy optic neuropathy cognitive decline.
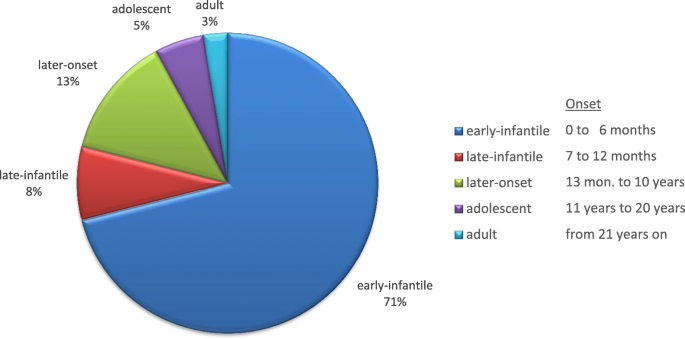
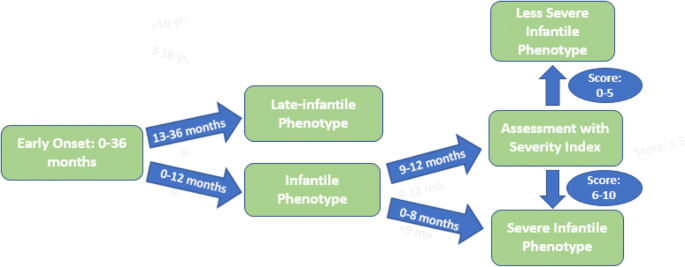
From a series of 11 patients. Symptoms of the later-onset types of Krabbe disease start in childhood early adolescence or adulthood. Characteristics of Krabbe disease in adultsKrabbe disease is a leukodystrophy where the severe form usually begins in early infancy during the first year of life and progresses rapidly.
In contrast adult patients usually present with progressive spastic paraparesis. Krabbe disease is considered a fatal disease and the average survival in the infantile type is 2 years. Most patients present within the first 6 months of life with infantile or classic disease manifest as extreme irritability spasticity and developmental delay Wenger et al 2000.
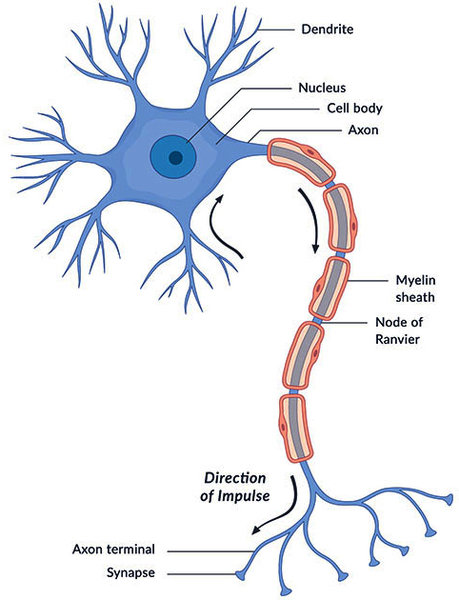
Head circumference may be diminished. 1 The condition has been mapped to chromosome 14q243-q321 and the GALC gene has recently been cloned. Krabbe disease also known as globoid cell leukodystrophy is an autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disorder resulting in damage to cells involved in myelin turnover.
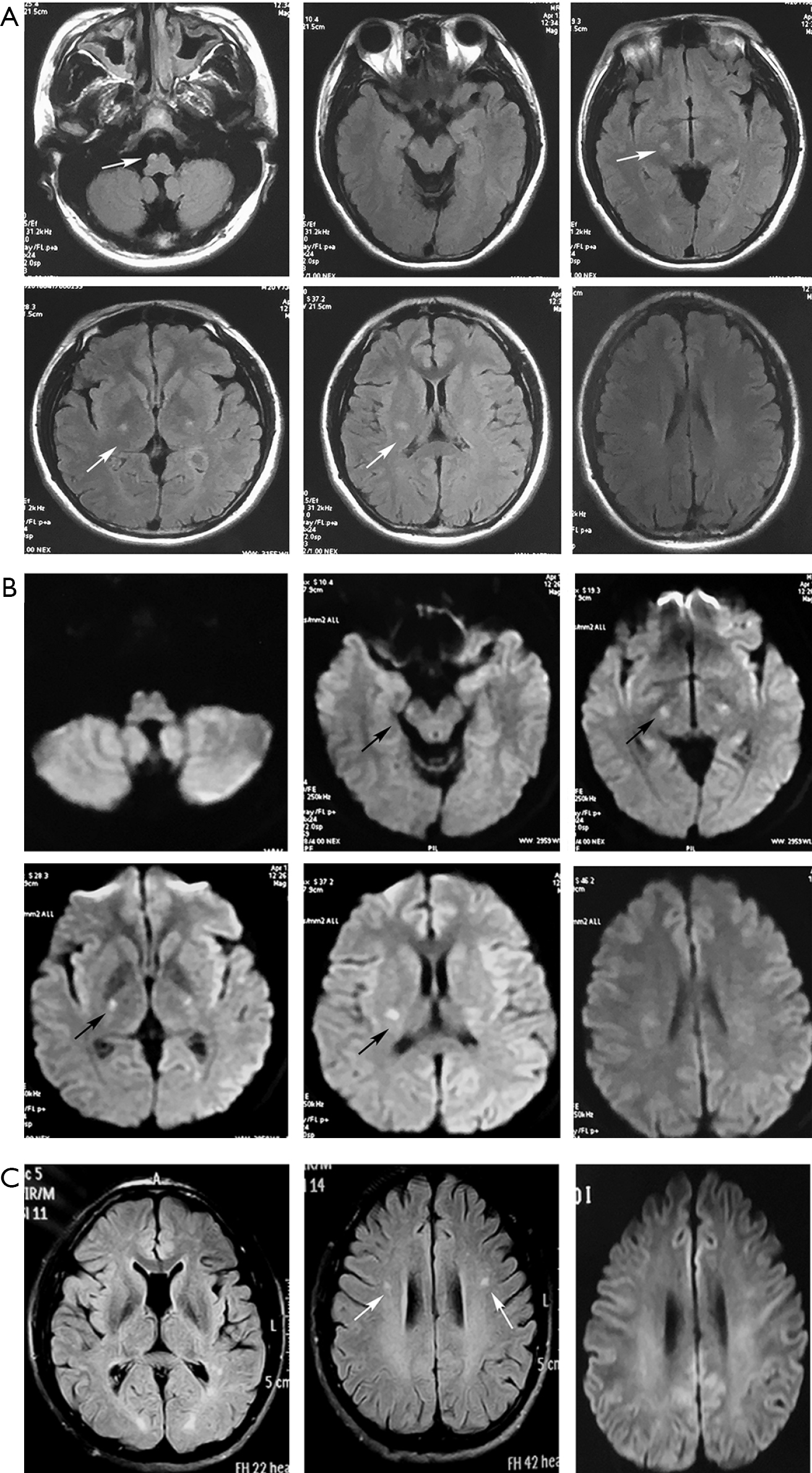
RABBE DISEASE or globoid cellleukodystrophyGLD is an autosomal recessive disordercausedbythede-ficiencyofgalactocerebro-sidase GALC activity12 While most pa-tientspresentwithsymptomsofspasticity developmental delay and irritability be-fore6monthsofagethedisorderhasalso been diagnosed in older patients includ-ing adults. Abstract and Figures Krabbe disease usually presents as a severe leukodystrophy in early infancy and childhood. The disease usually begins between the ages of 3 and 6 months with ambiguous symptoms such as irritability or hypersensitivity to external stimuli but soon progresses to severe mental and motor decline.
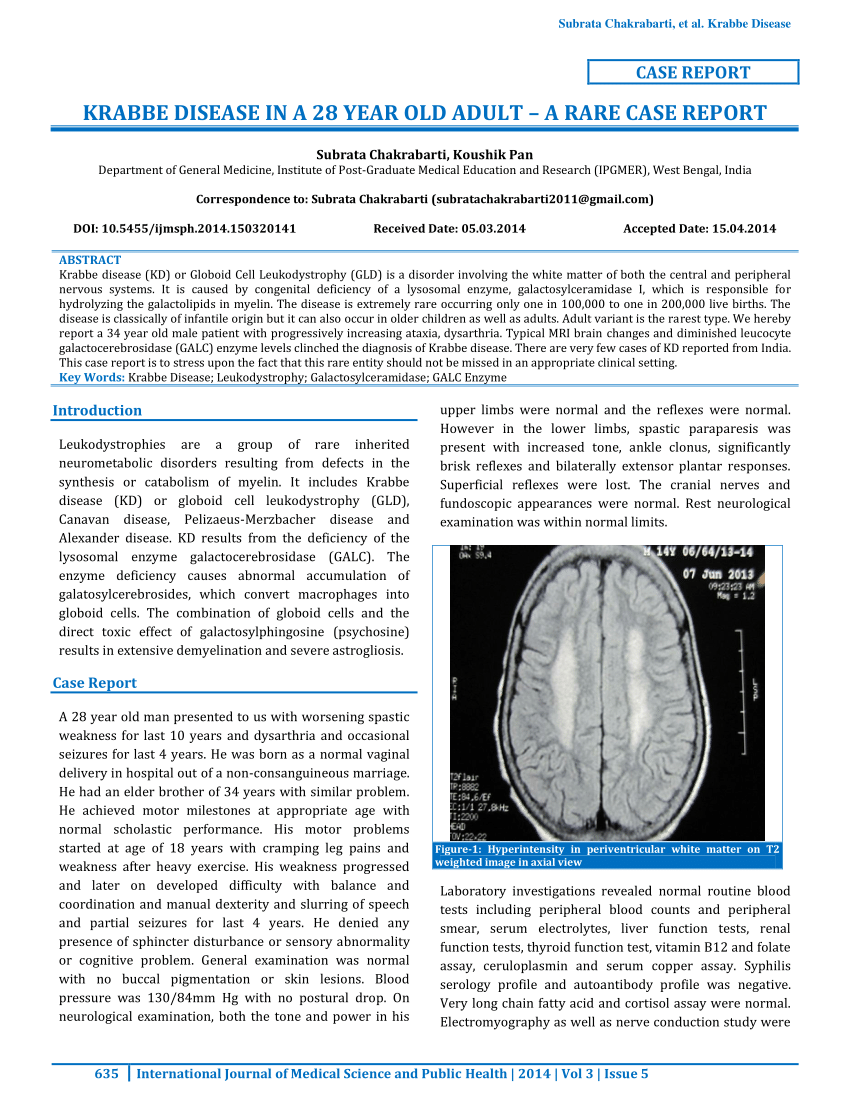
Globoid cell leukodystrophy or Krabbe disease is an autosomal recessive rapidly progressive fatal disease when it occurs in infancy. Krabbe disease symptoms Infantile Krabbe disease. Adult Krabbe disease can manifest as late as the 5th decade of life.
As the disease progresses signs and symptoms become more severe. Wenger et al 2001.
In contrast adult patients usually present with progressive spastic paraparesis.
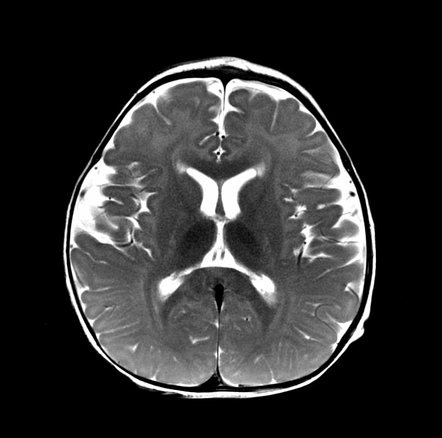
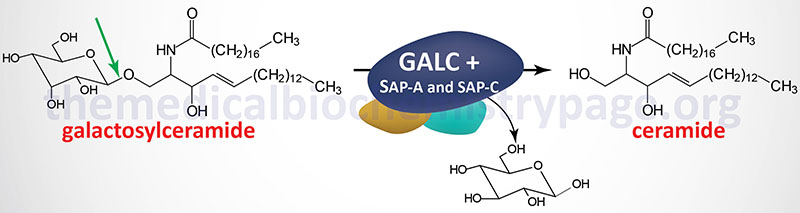
Symptoms of the later-onset types of Krabbe disease start in childhood early adolescence or adulthood. 23 Deficiency of GALC impairs cleavage of the galactose moiety from galactosylceramide. 1 The condition has been mapped to chromosome 14q243-q321 and the GALC gene has recently been cloned. Macular cherry red spots were reported in 1 patient. Globoid cell leukodystrophy or Krabbe disease is an autosomal recessive rapidly progressive fatal disease when it occurs in infancy. The disease usually begins between the ages of 3 and 6 months with ambiguous symptoms such as irritability or hypersensitivity to external stimuli but soon progresses to severe mental and motor decline. Other signs of the disease include peripheral neuropathy dysarthria cerebellar ataxia pes cavus deep sensory signs tongue atrophy optic neuropathy cognitive decline. LSDs occur when a part of the cell called the lysosome does not function properly. It thus affects both the peripheral nervous system and the central nervous system manifesting as a leukodystrophy.
The disease usually begins between the ages of 3 and 6 months with ambiguous symptoms such as irritability or hypersensitivity to external stimuli but soon progresses to severe mental and motor decline. Krabbe disease usually presents as a severe leukodystrophy in early infancy and childhood. LSDs occur when a part of the cell called the lysosome does not function properly. These may include muscle weakness and stiffness loss of milestones blindness behavior problems dementia and seizures. Krabbe disease also called globoid cell leukodystrophy GLD OMIM 245200 is an autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disease resulting from a deficiency of the lysosomal enzyme galactocerebrosidase galactosylceramidase GALC Suzuki and Suzuki 1970. Krabbe Disease is classified as both a Leukodystrophy and Lysosomal Storage Disorder LSD. Globoid cell leukodystrophy or Krabbe disease is an autosomal recessive rapidly progressive fatal disease when it occurs in infancy.
































Post a Comment for "Krabbe Disease In Adults"